This page was generated from a Jupyter notebook. You can view it on GitHub or download and run it locally.
Normal Inverse Gamma Distribution
This notebook demonstrates the Normal Inverse Gamma (NInvG) distribution, a normal variance-mean mixture where the mixing distribution is Inverse Gamma.
Mathematical Definition
The Normal Inverse Gamma distribution is defined as a normal mixture:
where:
\(\mu \in \mathbb{R}^d\): location parameter
\(\gamma \in \mathbb{R}^d\): skewness parameter
\(\Sigma \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times d}\): covariance scale matrix (positive definite)
\(\alpha > 0\): Inverse Gamma shape parameter
\(\beta > 0\): Inverse Gamma rate parameter
Key Properties
Property |
Formula |
Condition |
|---|---|---|
Mean |
\(E[X] = \mu + \gamma \frac{\beta}{\alpha - 1}\) |
\(\alpha > 1\) |
Covariance |
\(\text{Cov}[X] = \frac{\beta}{\alpha-1} \Sigma + \frac{\beta^2}{(\alpha-1)^2(\alpha-2)} \gamma \gamma^T\) |
\(\alpha > 2\) |
Distribution Types
Joint distribution \(f(x, y)\): Exponential family (tractable)
Marginal distribution \(f(x)\): NOT exponential family (requires EM for fitting)
Special Case
NInvG is a special case of the Generalized Hyperbolic distribution with GIG parameter \(a \to 0\).
When \(\gamma = 0\) (symmetric), NInvG is related to the Student-t distribution.
[1]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
from scipy import stats
from normix.distributions.mixtures import JointNormalInverseGamma, NormalInverseGamma
from normix.distributions.univariate import InverseGamma
from normix.utils import (
plot_joint_distribution_1d,
plot_marginal_distribution_2d,
validate_moments,
print_moment_validation,
fit_and_track_convergence,
plot_em_convergence,
test_joint_fitting,
print_fitting_results
)
plt.style.use('seaborn-v0_8-whitegrid')
%matplotlib inline
# Consistent styling
COLORS = {'primary': 'tab:blue', 'secondary': 'tab:red', 'tertiary': 'tab:green'}
np.set_printoptions(precision=4, suppress=True)
Parameter Sets for Testing
We test with three different parameter configurations to demonstrate the distribution’s flexibility.
Note: We need \(\alpha > 2\) for the variance to exist.
[2]:
# Define three parameter sets for comprehensive testing
PARAM_SETS = [
{
'name': 'Symmetric (γ=0)',
'mu': np.array([0.0, 0.0]),
'gamma': np.array([0.0, 0.0]),
'sigma': np.array([[1.0, 0.3], [0.3, 1.0]]),
'shape': 3.0, # α > 2 for finite variance
'rate': 1.0
},
{
'name': 'Right-skewed (γ>0)',
'mu': np.array([0.0, 0.0]),
'gamma': np.array([0.5, 0.3]),
'sigma': np.array([[1.0, 0.2], [0.2, 1.5]]),
'shape': 4.0,
'rate': 2.0
},
{
'name': 'Left-skewed (γ<0)',
'mu': np.array([1.0, -0.5]),
'gamma': np.array([-0.4, 0.2]),
'sigma': np.array([[2.0, -0.5], [-0.5, 1.0]]),
'shape': 5.0,
'rate': 1.5
}
]
# Display parameter sets
for i, params in enumerate(PARAM_SETS):
print(f"\nParameter Set {i+1}: {params['name']}")
print(f" μ = {params['mu']}")
print(f" γ = {params['gamma']}")
print(f" α = {params['shape']}, β = {params['rate']}")
Parameter Set 1: Symmetric (γ=0)
μ = [0. 0.]
γ = [0. 0.]
α = 3.0, β = 1.0
Parameter Set 2: Right-skewed (γ>0)
μ = [0. 0.]
γ = [0.5 0.3]
α = 4.0, β = 2.0
Parameter Set 3: Left-skewed (γ<0)
μ = [ 1. -0.5]
γ = [-0.4 0.2]
α = 5.0, β = 1.5
Part 1: Joint Distribution (1D X)
The joint distribution \(f(x, y)\) is an exponential family with natural parameters.
[3]:
def get_1d_params(params):
"""Extract 1D version of parameters."""
return {
'mu': np.array([params['mu'][0]]),
'gamma': np.array([params['gamma'][0]]),
'sigma': np.array([[params['sigma'][0, 0]]]),
'shape': params['shape'],
'rate': params['rate']
}
1.1 Joint Distribution Visualization
[4]:
N_SAMPLES = 5000
for i, params in enumerate(PARAM_SETS):
params_1d = get_1d_params(params)
joint_dist = JointNormalInverseGamma.from_classical_params(**params_1d)
print(f"\n{'='*70}")
print(f"Parameter Set {i+1}: {params['name']}")
print(f"{'='*70}")
fig = plot_joint_distribution_1d(
joint_dist,
n_samples=N_SAMPLES,
random_state=42,
title=f"Joint Normal Inverse Gamma - {params['name']}"
)
plt.show()
======================================================================
Parameter Set 1: Symmetric (γ=0)
======================================================================
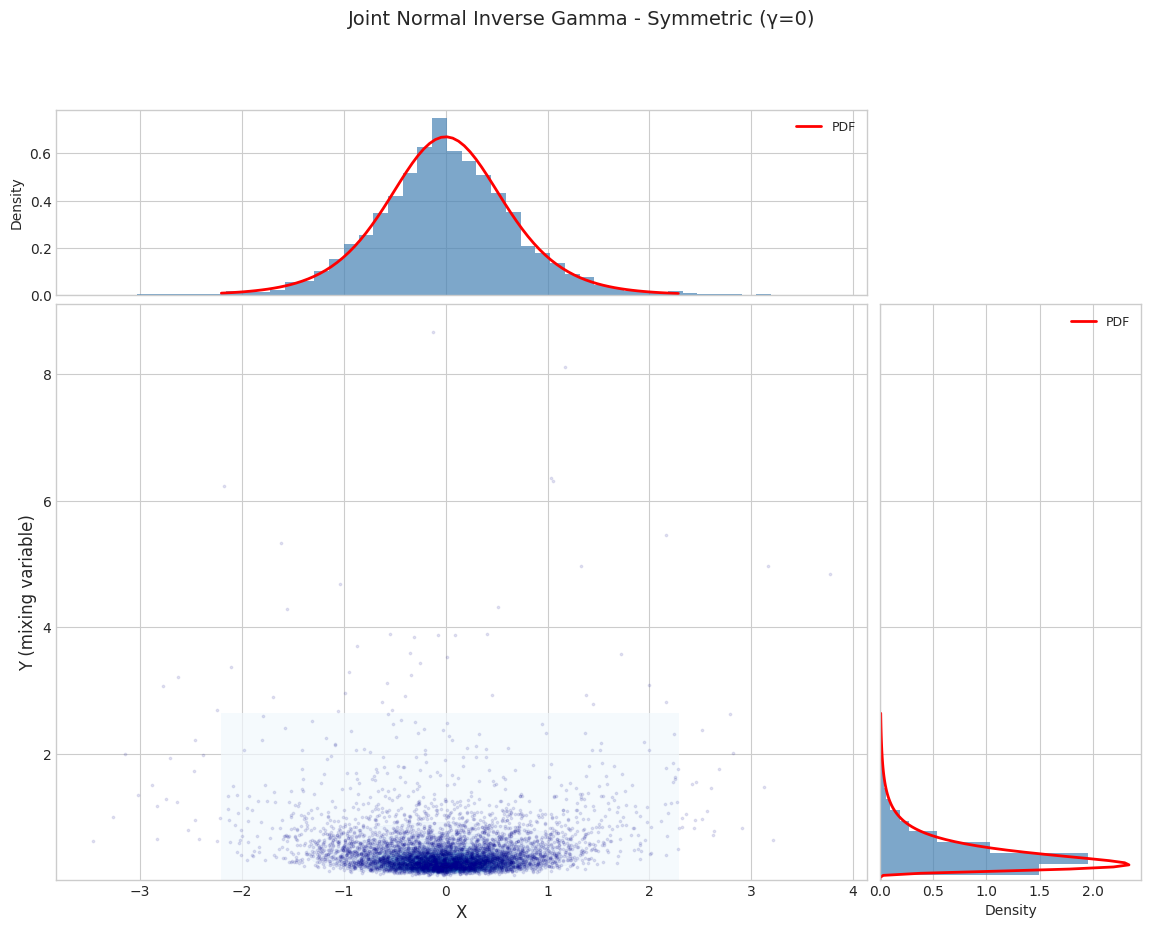
======================================================================
Parameter Set 2: Right-skewed (γ>0)
======================================================================
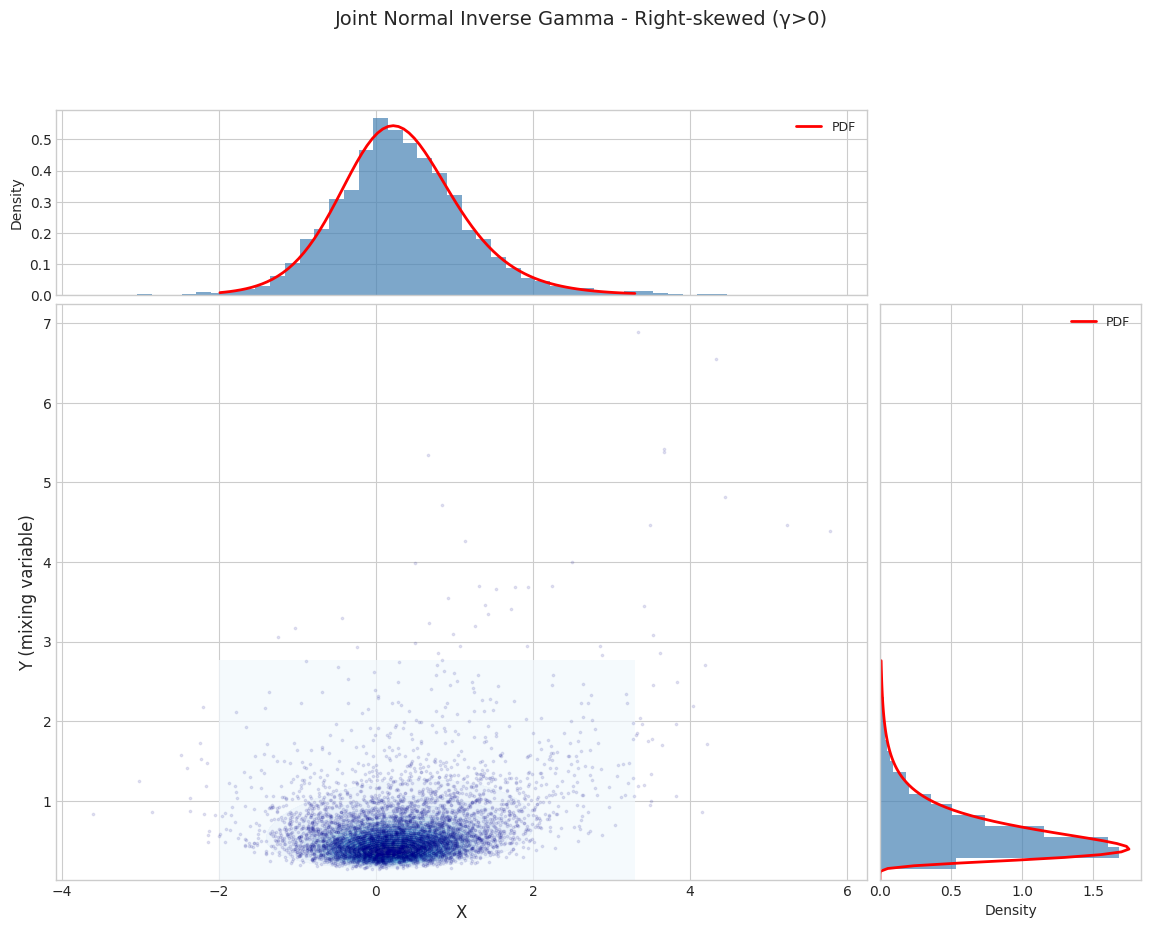
======================================================================
Parameter Set 3: Left-skewed (γ<0)
======================================================================
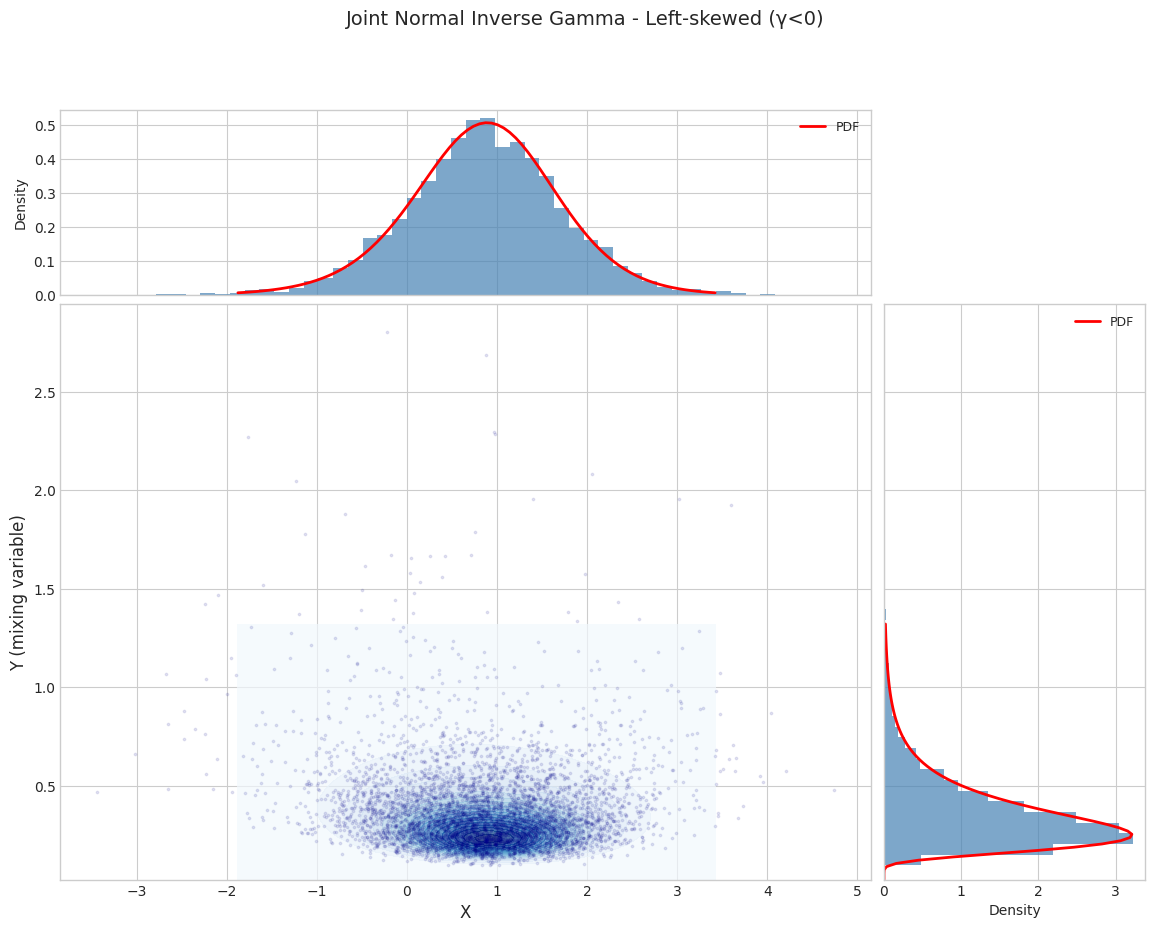
1.2 Moment Validation (Joint)
[5]:
for i, params in enumerate(PARAM_SETS):
params_1d = get_1d_params(params)
joint_dist = JointNormalInverseGamma.from_classical_params(**params_1d)
results = validate_moments(joint_dist, n_samples=50000, random_state=42, is_joint=True)
print_moment_validation(results, f"Joint NInvG - {params['name']}")
============================================================
Moment Validation: Joint NInvG - Symmetric (γ=0)
============================================================
X_mean : sample = -0.0060, theory = 0.0000, rel_err = 6.03e+07
Y_mean : sample = 0.5012, theory = 0.5000, rel_err = 2.39e-03
X_var : sample = 0.5016, theory = 0.5000, rel_err = 3.12e-03
Y_var : sample = 0.2557, theory = 0.2500, rel_err = 2.27e-02
============================================================
Moment Validation: Joint NInvG - Right-skewed (γ>0)
============================================================
X_mean : sample = 0.3268, theory = 0.3333, rel_err = 1.96e-02
Y_mean : sample = 0.6677, theory = 0.6667, rel_err = 1.60e-03
X_var : sample = 0.7274, theory = 0.7222, rel_err = 7.17e-03
Y_var : sample = 0.2266, theory = 0.2222, rel_err = 1.99e-02
============================================================
Moment Validation: Joint NInvG - Left-skewed (γ<0)
============================================================
X_mean : sample = 0.8423, theory = 0.8500, rel_err = 9.09e-03
Y_mean : sample = 0.3755, theory = 0.3750, rel_err = 1.28e-03
X_var : sample = 0.7622, theory = 0.7575, rel_err = 6.23e-03
Y_var : sample = 0.0475, theory = 0.0469, rel_err = 1.32e-02
1.3 Joint Distribution Fitting (Exponential Family MLE)
[6]:
for i, params in enumerate(PARAM_SETS):
params_1d = get_1d_params(params)
fitted_dist, fitted_params, param_errors = test_joint_fitting(
JointNormalInverseGamma,
params_1d,
n_samples=N_SAMPLES,
random_state=42
)
print_fitting_results(params_1d, fitted_params, param_errors, f"Joint NInvG - {params['name']}")
============================================================
Fitting Results: Joint NInvG - Symmetric (γ=0)
============================================================
Parameter True Fitted Rel.Error
------------------------------------------------------------
mu 0.0000 -0.0147 1.47e+08
gamma 0.0000 0.0328 3.28e+08
sigma 1.0000 1.0242 2.42e-02
shape 3.0000 3.0147 4.90e-03
rate 1.0000 0.9999 9.66e-05
============================================================
Fitting Results: Joint NInvG - Right-skewed (γ>0)
============================================================
Parameter True Fitted Rel.Error
------------------------------------------------------------
mu 0.0000 -0.0209 2.09e+08
gamma 0.5000 0.5333 6.65e-02
sigma 1.0000 1.0242 2.42e-02
shape 4.0000 4.0180 4.50e-03
rate 2.0000 2.0000 2.17e-05
============================================================
Fitting Results: Joint NInvG - Left-skewed (γ<0)
============================================================
Parameter True Fitted Rel.Error
------------------------------------------------------------
mu 1.0000 0.9743 2.57e-02
gamma -0.4000 -0.3292 1.77e-01
sigma 2.0000 2.0485 2.42e-02
shape 5.0000 5.0211 4.21e-03
rate 1.5000 1.5002 1.29e-04
Part 2: Marginal Distribution (2D X)
The marginal distribution \(f(x) = \int f(x, y) dy\) is NOT an exponential family.
Fitting requires the EM algorithm.
2.1 Marginal Distribution Visualization
[7]:
for i, params in enumerate(PARAM_SETS):
marginal_dist = NormalInverseGamma.from_classical_params(**params)
print(f"\n{'='*70}")
print(f"Parameter Set {i+1}: {params['name']}")
print(f"{'='*70}")
fig = plot_marginal_distribution_2d(
marginal_dist,
n_samples=N_SAMPLES,
random_state=42,
title=f"Marginal Normal Inverse Gamma (2D) - {params['name']}"
)
plt.show()
======================================================================
Parameter Set 1: Symmetric (γ=0)
======================================================================
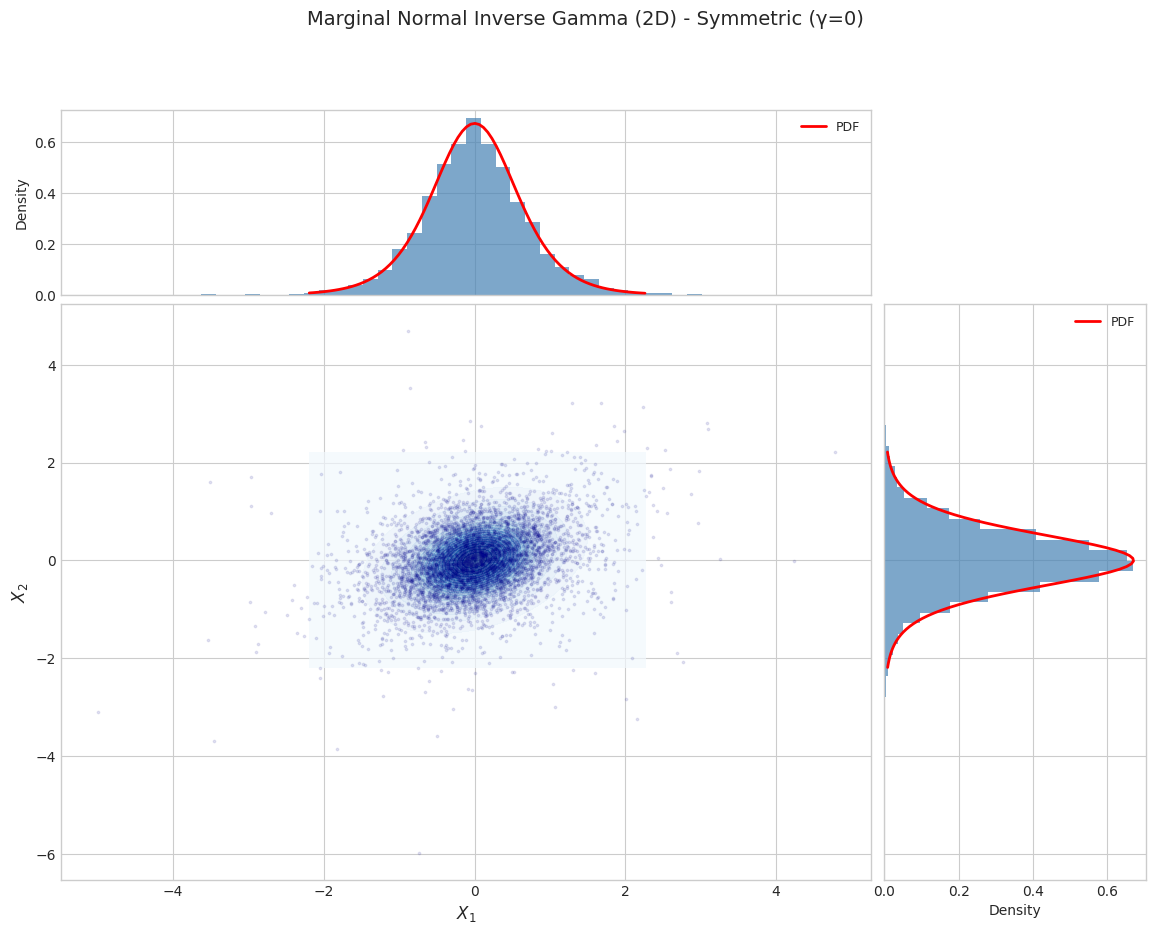
======================================================================
Parameter Set 2: Right-skewed (γ>0)
======================================================================
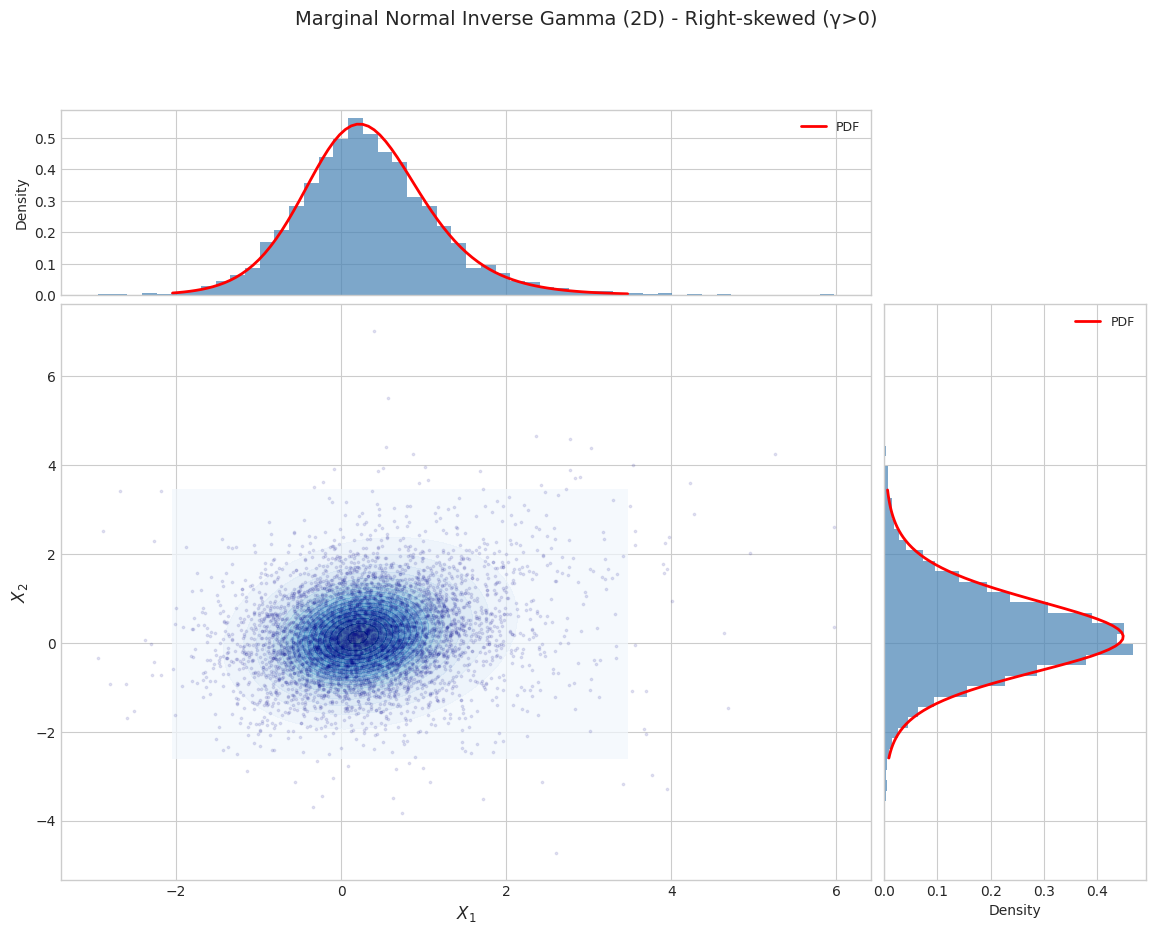
======================================================================
Parameter Set 3: Left-skewed (γ<0)
======================================================================
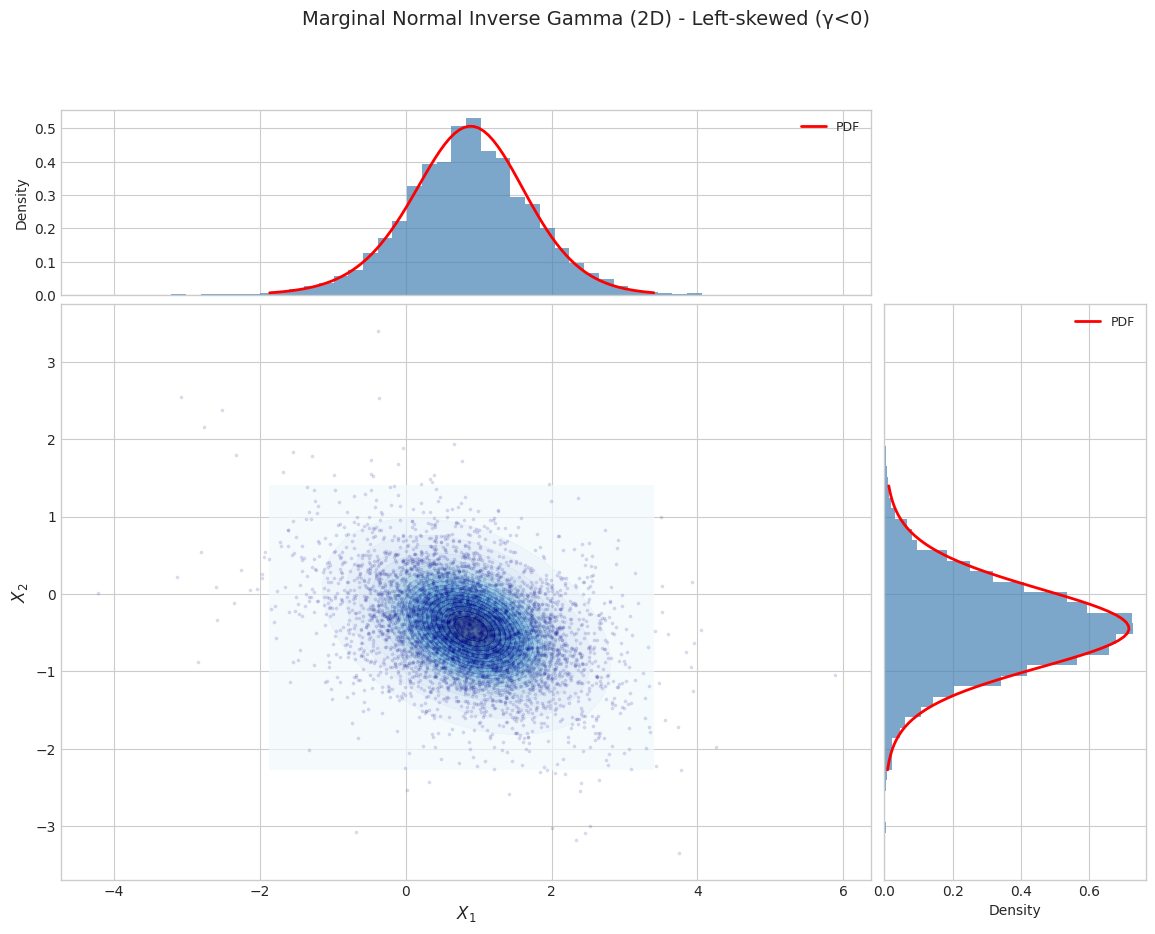
2.2 Moment Validation (Marginal)
[8]:
for i, params in enumerate(PARAM_SETS):
marginal_dist = NormalInverseGamma.from_classical_params(**params)
results = validate_moments(marginal_dist, n_samples=50000, random_state=42, is_joint=False)
print_moment_validation(results, f"Marginal NInvG - {params['name']}")
============================================================
Moment Validation: Marginal NInvG - Symmetric (γ=0)
============================================================
mean :
sample = [-0.0077 -0.0051]
theory = [0. 0.]
rel_err = [77307132.17 51282875.38]
variance :
sample = [0.5132 0.5074]
theory = [0.5 0.5]
rel_err = [0.03 0.01]
============================================================
Moment Validation: Marginal NInvG - Right-skewed (γ>0)
============================================================
mean :
sample = [0.3252 0.195 ]
theory = [0.3333 0.2 ]
rel_err = [0.02 0.03]
variance :
sample = [0.7318 1.0234]
theory = [0.7222 1.02 ]
rel_err = [0.01 0. ]
============================================================
Moment Validation: Marginal NInvG - Left-skewed (γ<0)
============================================================
mean :
sample = [ 0.8409 -0.4246]
theory = [ 0.85 -0.425]
rel_err = [0.01 0. ]
variance :
sample = [0.7763 0.3804]
theory = [0.7575 0.3769]
rel_err = [0.02 0.01]
2.3 EM Algorithm Fitting with Convergence Tracking
[9]:
for i, params in enumerate(PARAM_SETS):
print(f"\n{'='*70}")
print(f"Parameter Set {i+1}: {params['name']}")
print(f"{'='*70}")
# Generate data from true distribution
true_dist = NormalInverseGamma.from_classical_params(**params)
X_data = true_dist.rvs(size=N_SAMPLES, random_state=42)
# Fit with EM and track convergence
fitted_dist, convergence = fit_and_track_convergence(
NormalInverseGamma,
X_data,
max_iter=100,
random_state=43
)
# Print results
print(f"\nConverged: {convergence.converged}")
print(f"Iterations: {len(convergence.iterations)}")
if convergence.log_likelihoods:
print(f"Initial LL: {convergence.log_likelihoods[0]:.4f}")
print(f"Final LL: {convergence.log_likelihoods[-1]:.4f}")
# Compare parameters
print("\nParameter Comparison:")
print(f" True α = {params['shape']:.4f}, Fitted α = {convergence.final_params['shape']:.4f}")
print(f" True β = {params['rate']:.4f}, Fitted β = {convergence.final_params['rate']:.4f}")
# Plot convergence
if convergence.iterations:
fig = plot_em_convergence(
convergence,
title=f"EM Convergence - {params['name']}"
)
plt.show()
======================================================================
Parameter Set 1: Symmetric (γ=0)
======================================================================
Converged: True
Iterations: 25
Initial LL: -2.0314
Final LL: -2.0305
Parameter Comparison:
True α = 3.0000, Fitted α = 2.7743
True β = 1.0000, Fitted β = 0.9147
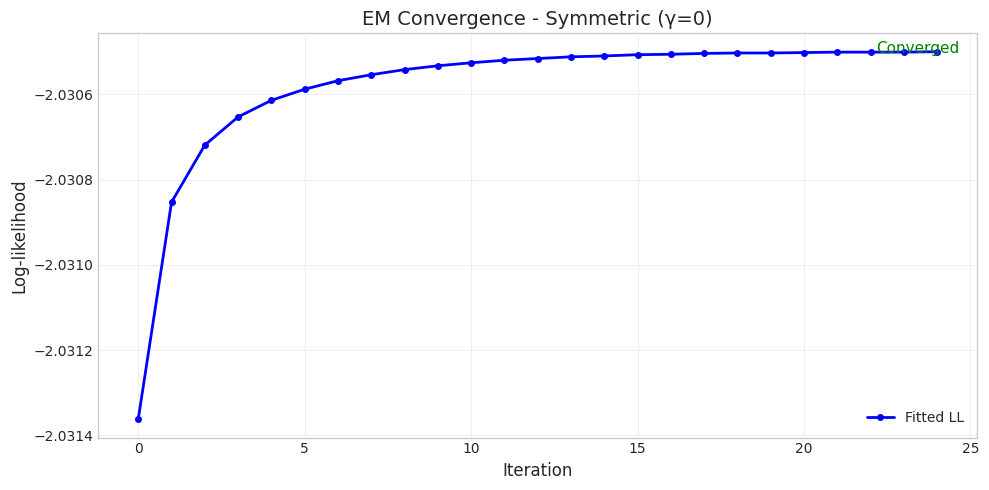
======================================================================
Parameter Set 2: Right-skewed (γ>0)
======================================================================
Converged: True
Iterations: 68
Initial LL: -2.6262
Final LL: -2.6144
Parameter Comparison:
True α = 4.0000, Fitted α = 3.5385
True β = 2.0000, Fitted β = 1.1895
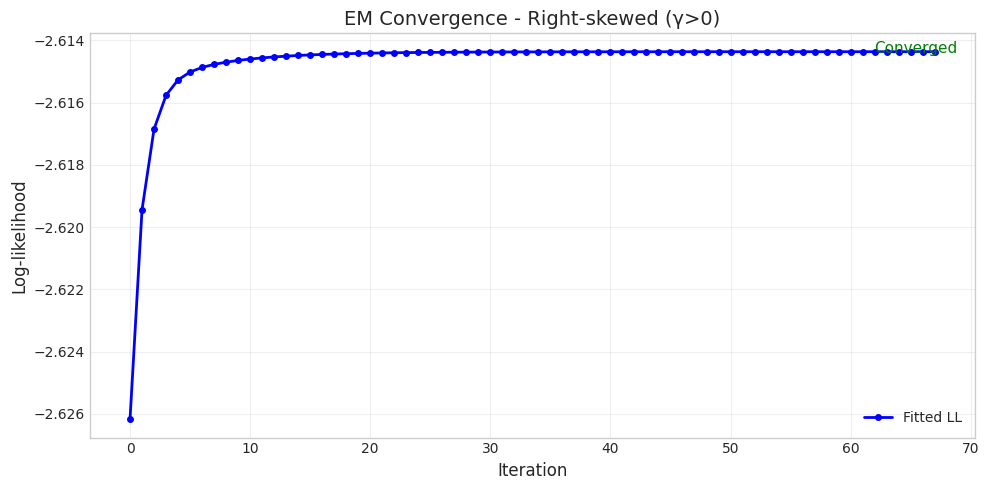
======================================================================
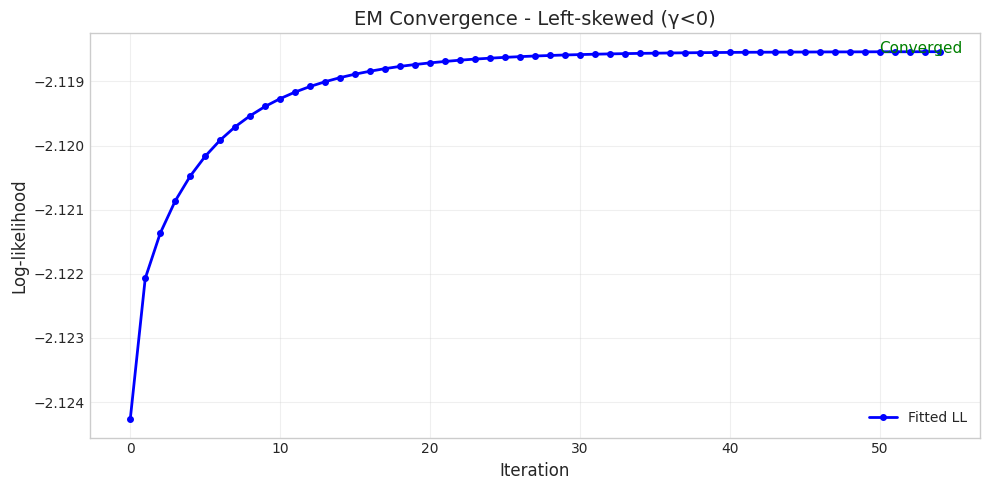
Parameter Set 3: Left-skewed (γ<0)
======================================================================
Converged: True
Iterations: 55
Initial LL: -2.1243
Final LL: -2.1185
Parameter Comparison:
True α = 5.0000, Fitted α = 4.4515
True β = 1.5000, Fitted β = 1.5368
Part 3: Exponential Family Structure
The joint distribution has the exponential family form:
[11]:
# Demonstrate exponential family structure
params_1d = get_1d_params(PARAM_SETS[1]) # Use right-skewed set
joint_dist = JointNormalInverseGamma.from_classical_params(**params_1d)
print("Exponential Family Structure")
print("="*60)
print(f"\nClassical parameters:")
print(joint_dist.classical_params)
print(f"\nNatural parameters θ:")
print(joint_dist.natural_params)
print(f"\nExpectation parameters η = E[t(X,Y)]:")
print(joint_dist.expectation_params)
Exponential Family Structure
============================================================
Classical parameters:
{'mu': array([0.]), 'gamma': array([0.5]), 'sigma': array([[1.]]), 'shape': np.float64(4.0), 'rate': np.float64(2.0)}
Natural parameters θ:
[-5.5 -2. -0.125 0.5 0. -0.5 ]
Expectation parameters η = E[t(X,Y)]:
[-0.563 2. 0.6667 0.3333 0.5 1.1667]
[13]:
# Verify E[t(X,Y)] matches expectation parameters
X_samples, Y_samples = joint_dist.rvs(size=50000, random_state=42)
t_samples = joint_dist._sufficient_statistics(X_samples, Y_samples)
eta_sample = np.mean(t_samples, axis=0)
eta_theory = joint_dist.expectation_params
print("\nVerification: E[t(X,Y)] from samples vs theory")
print("="*60)
print(f"Sample: {eta_sample}")
print(f"Theory: {eta_theory}")
print(f"Max error: {np.max(np.abs(eta_sample - eta_theory)):.6f}")
Verification: E[t(X,Y)] from samples vs theory
============================================================
Sample: [-0.5618 1.9985 0.6677 0.3268 0.4892 1.1688]
Theory: [-0.563 2. 0.6667 0.3333 0.5 1.1667]
Max error: 0.010790
Part 4: Connection to Student-t (Symmetric Case)
When \(\gamma = 0\), the NInvG distribution is symmetric and related to the Student-t distribution.
[14]:
# Compare symmetric NInvG with Normal and Student-t
params_sym = PARAM_SETS[0] # Symmetric case
ninvg = NormalInverseGamma.from_classical_params(
mu=np.array([0.0]),
gamma=np.array([0.0]),
sigma=np.array([[1.0]]),
shape=3.0,
rate=1.0
)
# Sample and compute statistics
samples = ninvg.rvs(size=50000, random_state=42)
# Compare with Normal and Student-t
ninvg_mean = ninvg.mean()[0]
ninvg_var = ninvg.var()[0]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
x_range = np.linspace(-5, 5, 300)
# PDF comparison
ninvg_pdf = ninvg.pdf(x_range.reshape(-1, 1)).flatten()
normal_pdf = stats.norm(loc=ninvg_mean, scale=np.sqrt(ninvg_var)).pdf(x_range)
# Student-t with df = 2α for comparison
t_pdf = stats.t(df=6, loc=ninvg_mean, scale=np.sqrt(ninvg_var * 4/6)).pdf(x_range)
axes[0].plot(x_range, ninvg_pdf, 'b-', linewidth=2, label='NInvG')
axes[0].plot(x_range, normal_pdf, 'r--', linewidth=2, label='Normal')
axes[0].plot(x_range, t_pdf, 'g:', linewidth=2, label='Student-t (df=6)')
axes[0].set_xlabel('X')
axes[0].set_ylabel('Density')
axes[0].set_title('PDF Comparison')
axes[0].legend()
# Log-scale for tails
axes[1].semilogy(x_range, ninvg_pdf, 'b-', linewidth=2, label='NInvG')
axes[1].semilogy(x_range, normal_pdf, 'r--', linewidth=2, label='Normal')
axes[1].semilogy(x_range, t_pdf, 'g:', linewidth=2, label='Student-t (df=6)')
axes[1].set_xlabel('X')
axes[1].set_ylabel('Density (log scale)')
axes[1].set_title('Tail Comparison (Log Scale)')
axes[1].legend()
plt.suptitle('Symmetric NInvG vs Normal and Student-t', fontsize=14)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print(f"\nNInvG: mean = {ninvg_mean:.4f}, var = {ninvg_var:.4f}")
print(f"Sample kurtosis: {stats.kurtosis(samples.flatten()):.4f} (normal = 0)")
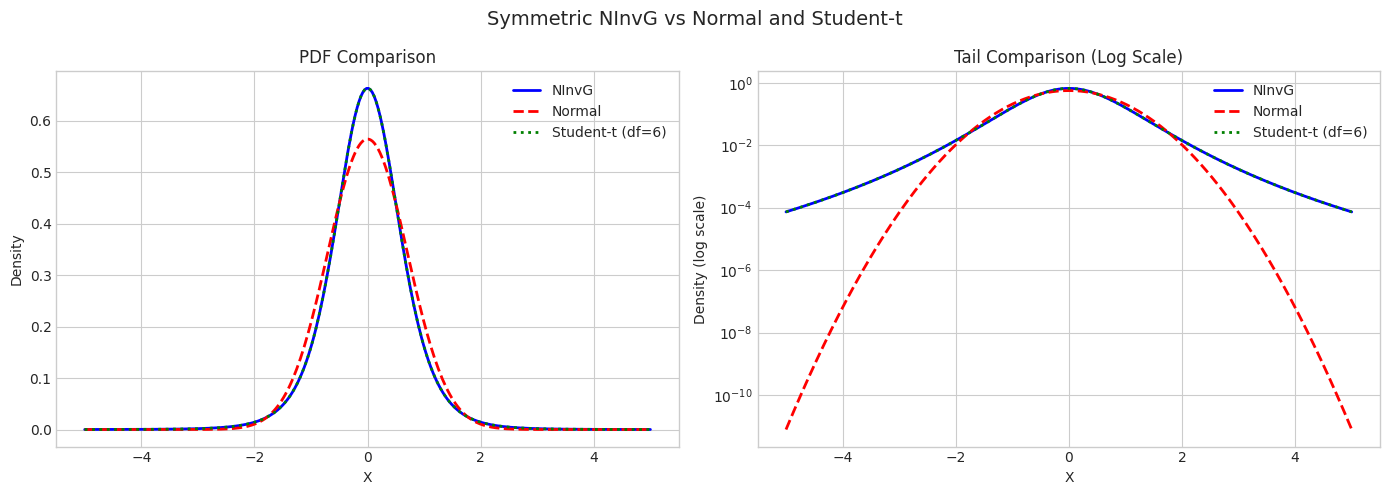
NInvG: mean = 0.0000, var = 0.5000
Sample kurtosis: 2.3420 (normal = 0)
Summary
The Normal Inverse Gamma distribution is a flexible model with:
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
Mixing |
\(Y \sim \text{InvGamma}(\alpha, \beta)\) |
Skewness |
Controlled by \(\gamma\) |
Tail behavior |
Heavy tails (Student-t like when \(\gamma=0\)) |
Joint fitting |
Exponential family MLE |
Marginal fitting |
EM algorithm |
Constraints |
\(\alpha > 1\) for mean, \(\alpha > 2\) for variance |